
Scientists have developed a breakthrough optical technology that could dramatically enhance the capacity and security of data transmission (Fig. 1). By utilizing a new type of spatial-frequency patching metasurface that manipulates light beams, researchers have introduced what they call “super-capacity perfect vector vortex beams” (SC-PVVBs). These light beams, which possess intricate spatial and polarization characteristics, can carry vast amounts of information, making them ideal for dense data communication systems.
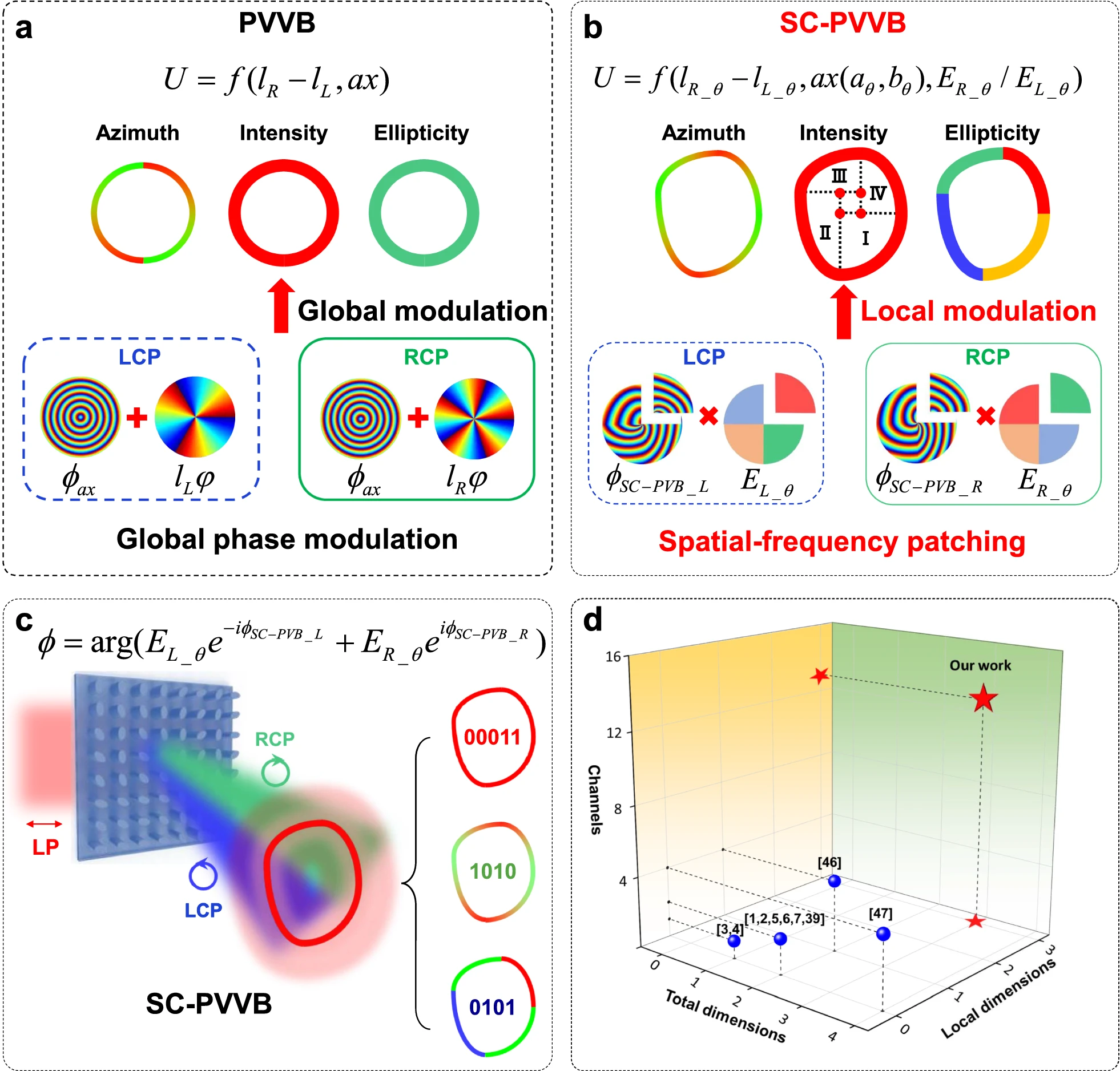
Conventional optical beams often have limitations in terms of data capacity due to the global phase modulation approach. However, the SC-PVVB technology overcomes these restrictions by locally patching the spatial frequency to create multiple data channels, each of which can independently store and transmit information.
The new approach enables precise control over the beam’s structure and polarization, allowing for at least 13 distinct data channels (Fig. 2). This could lead to ultra-secure and high-capacity optical communication systems.
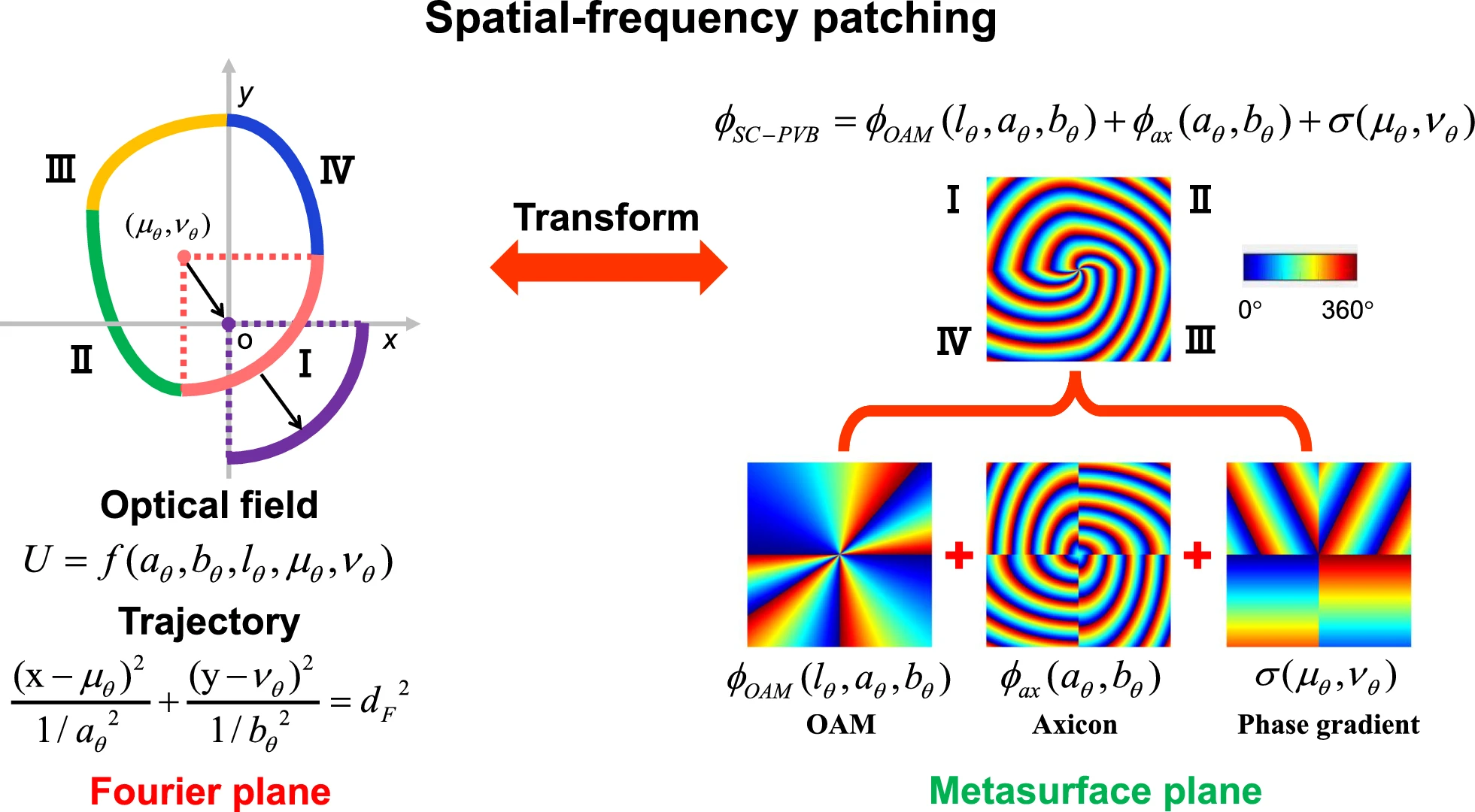
One of the key innovations is the ability to control the spatial intensity and polarization of these beams on a local scale, allowing information to be embedded across three dimensions of the light beam. Researchers used a specially designed Dammann grating to generate arrays of SC-PVVBs, maximizing their data-carrying potential.
The potential applications of this technology go beyond data transmission, with implications for optical encryption, secure communications, and even particle manipulation. With a capacity to handle large data volumes while ensuring robust security, SC-PVVBs represent a significant advancement in optical information technology, paving the way for future innovations in communication and encryption systems.
